For dogs the ideal dosage of Vitamin B Complex 100 ml injectable is 0.5 to 2 mL.
Vitamin B Complex Dosage For Dogs

-
Ideal Dosage: 0.5 to 2 mL (100 ml injectable)
-
Uses: Vitamin B deficiencies
-
FDA Approved: NO
-
Storage & Handling: 36-46 degrees Fahrenheit and out of direct sunlight.
-
Dosage and Administration: Vet Recommendation
-
Variants: Tablets, Injectable
As devoted pet owners, ensuring our furry companions lead healthy, vibrant lives is a top priority. Amidst the myriad dietary supplements available, Vitamin B Complex is crucial in maintaining optimal health for our four-legged friends.
From supporting energy metabolism to bolstering immune function, the benefits are undeniable. However, determining the correct dosage for our beloved canines can be perplexing.
What is Vitamin B Complex?
Vitamin B complex is a group of water-soluble vitamins that play essential roles in various bodily functions. This group typically includes eight B vitamins:
-
B1 (Thiamine): Helps convert food into energy and supports nerve function.
-
B2 (Riboflavin): Important for energy production, metabolism, and healthy skin and eyes.
-
B3 (Niacin): Plays a role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and skin health.
-
B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Necessary for synthesizing hormones and breaking down fats and carbohydrates for energy.
-
B6 (Pyridoxine): Involved in amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, and immune function.
-
B7 (Biotin): Supports metabolism, cell growth, and the health of skin, hair, and nails.
-
B9 (Folate or Folic Acid): Vital for DNA synthesis, cell division, and the formation of red blood cells.
-
B12 (Cobalamin): Essential for nerve function, DNA synthesis, red blood cell formation, and energy metabolism.
Vitamin B Complex Dosage For Dogs
The daily recommended intake of B-complex vitamins for a 30-pound dog varies depending on their calorie intake. It is suggested that 0.56 mg of thiamine be consumed per 1,000 calories. Riboflavin should be given at 1.3 mg per 1,000 calories, while niacin requires 4 mg per 1,000 calories.
Folic acid intake should be 68 micrograms per 1,000 calories, and pantothenic acid at 4 mg per 1,000 calories. Biotin is recommended at 7 mg per 1,000 calories, pyridoxine at 0.4 mg per 1,000 calories, and cobalamin at 9 micrograms per 1,000 calories.
These guidelines help ensure adequate vitamin intake to support the dog’s health and well-being.
Disclaimer: Self-medication can be hazardous. Please consult your veterinarian for personalized guidance on the appropriate dosage for your furry friend’s specific condition.
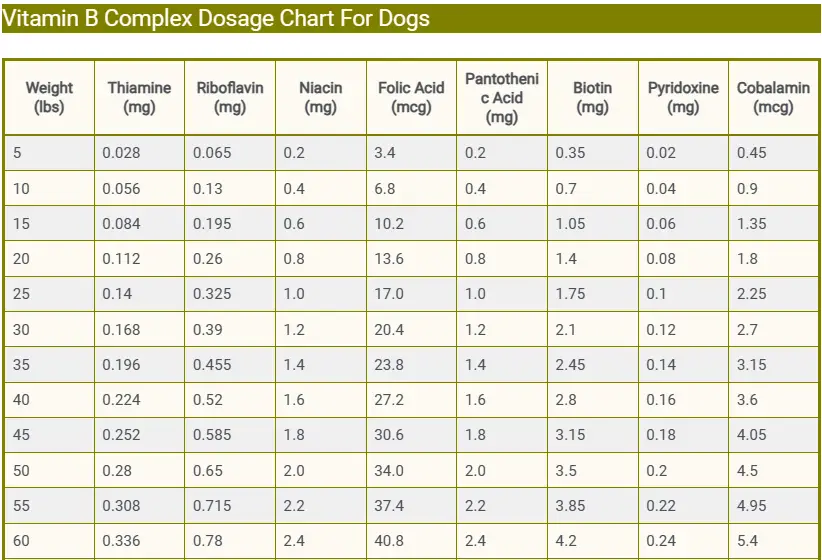
Vitamin B Complex Dosage Chart For Dogs
| Weight (lbs) | Thiamine (mg) | Riboflavin (mg) | Niacin (mg) | Folic Acid (mcg) | Pantothenic Acid (mg) | Biotin (mg) | Pyridoxine (mg) | Cobalamin (mcg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.028 | 0.065 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 0.35 | 0.02 | 0.45 |
| 10 | 0.056 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 6.8 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.04 | 0.9 |
| 15 | 0.084 | 0.195 | 0.6 | 10.2 | 0.6 | 1.05 | 0.06 | 1.35 |
| 20 | 0.112 | 0.26 | 0.8 | 13.6 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.08 | 1.8 |
| 25 | 0.14 | 0.325 | 1.0 | 17.0 | 1.0 | 1.75 | 0.1 | 2.25 |
| 30 | 0.168 | 0.39 | 1.2 | 20.4 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 0.12 | 2.7 |
| 35 | 0.196 | 0.455 | 1.4 | 23.8 | 1.4 | 2.45 | 0.14 | 3.15 |
| 40 | 0.224 | 0.52 | 1.6 | 27.2 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 0.16 | 3.6 |
| 45 | 0.252 | 0.585 | 1.8 | 30.6 | 1.8 | 3.15 | 0.18 | 4.05 |
| 50 | 0.28 | 0.65 | 2.0 | 34.0 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| 55 | 0.308 | 0.715 | 2.2 | 37.4 | 2.2 | 3.85 | 0.22 | 4.95 |
| 60 | 0.336 | 0.78 | 2.4 | 40.8 | 2.4 | 4.2 | 0.24 | 5.4 |
| 65 | 0.364 | 0.845 | 2.6 | 44.2 | 2.6 | 4.55 | 0.26 | 5.85 |
| 70 | 0.392 | 0.91 | 2.8 | 47.6 | 2.8 | 4.9 | 0.28 | 6.3 |
| 75 | 0.42 | 0.975 | 3.0 | 51.0 | 3.0 | 5.25 | 0.3 | 6.75 |
| 80 | 0.448 | 1.04 | 3.2 | 54.4 | 3.2 | 5.6 | 0.32 | 7.2 |
| 85 | 0.476 | 1.105 | 3.4 | 57.8 | 3.4 | 5.95 | 0.34 | 7.65 |
| 90 | 0.504 | 1.17 | 3.6 | 61.2 | 3.6 | 6.3 | 0.36 | 8.1 |
| 95 | 0.532 | 1.235 | 3.8 | 64.6 | 3.8 | 6.65 | 0.38 | 8.55 |
| 100 | 0.56 | 1.3 | 4.0 | 68.0 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 0.4 | 9.0 |
Related Post: Thyro Tabs Dosage For Dogs
Uses
-
Energy Metabolism: B vitamins support the conversion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy, promoting vitality.
-
Nervous System Function: Certain B vitamins maintain a healthy nervous system, supporting nerve function and overall neurological health.
-
Skin and Coat Health: Biotin contributes to healthy skin, hair, and nails, promoting a shiny coat.
-
Digestive Health: B vitamins aid in nutrient metabolism and support proper gastrointestinal function.
-
Immune System Support: B vitamins help produce antibodies and white blood cells, supporting immune function.
-
Stress Management: B vitamins assist in regulating hormone levels and neurotransmitter activity, helping dogs cope with stress and anxiety.
Potential Side Effects
-
Gastrointestinal Upset: Excessive intake of certain B vitamins like niacin (B3) can lead to digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort.
-
Allergic Reactions: Dogs may develop allergic reactions to components of vitamin B complex supplements, resulting in symptoms like itching, swelling, or hives.
-
Hypersensitivity: Some dogs may show hypersensitivity reactions to vitamin B complex supplements, including lethargy, weakness, or behavioral changes.
-
Interference with Medications: High doses of certain B vitamins, such as vitamin B6, can interfere with the absorption or efficacy of medications, potentially causing adverse effects or reduced effectiveness.
-
Risk of Overdose: While water-soluble vitamins are usually excreted in urine if consumed in excess, prolonged or extreme overdoses can still lead to toxicity symptoms like neurological issues, liver damage, or metabolic imbalances.
Related Post: Vetprofen Dosage For Dogs









![Can Dogs Eat Blood? 7 Side Effects [Expert Opinion]](https://petskor.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Webp.net-resizeimage-12.jpg)
