The safe minimum dosage of aspirin for dogs is 10mg/kg every 12 hours. However, for treating specific conditions, the dose can be increased to 40mg/kg. Overdosing on aspirin can be toxic to canines, so make sure to administer the ideal dose with advice from a veterinarian only.
Aspirin Dosage For Dogs

-
Ideal Dose: 10-40mg/kg (4-18 mg/lb)
-
Uses: Osteoarthritis, Musculoskeletal inflammation.
-
FDA Approved: No.
-
Variants: Tablets.
-
Storage & Handling: Room Temperature.
-
Administration: Every 12 hours
Disclaimer: Self-medication can be hazardous. Please consult your veterinarian for personalized guidance on the appropriate dosage for your furry friend’s specific condition.
As responsible pet owners, ensuring the health and well-being of our furry companions is paramount. However, just like humans, dogs can experience pain and discomfort for various reasons, whether arthritis, injury, or post-operative recovery. In such cases, many dog owners turn to aspirin as a solution.
Yet, administering this common over-the-counter medication to our four-legged friends requires careful consideration and understanding of the appropriate dosage.
This article delves into the intricacies of aspirin usage for dogs, including dosage guidelines, potential risks, and important considerations every pet owner should know to keep their beloved canine companions safe and healthy.
Aspirin Dosage For Dogs
The aspirin dosage for dogs can vary depending on their size, weight, and medical condition. It’s crucial to consult a veterinarian before administering any medication to your dog, including aspirin.
Aspirin dosage in dogs is approximately 10-40mg/kg (4-18 mg/lb) of body weight, given every 12 hours. However, this dosage can vary, and following your vet’s recommendations is important. Also, never give your dog coated aspirin, as the coating can harm dogs.
Always use plain aspirin and avoid giving it to dogs with certain health conditions or those taking other medications without consulting a veterinarian first.
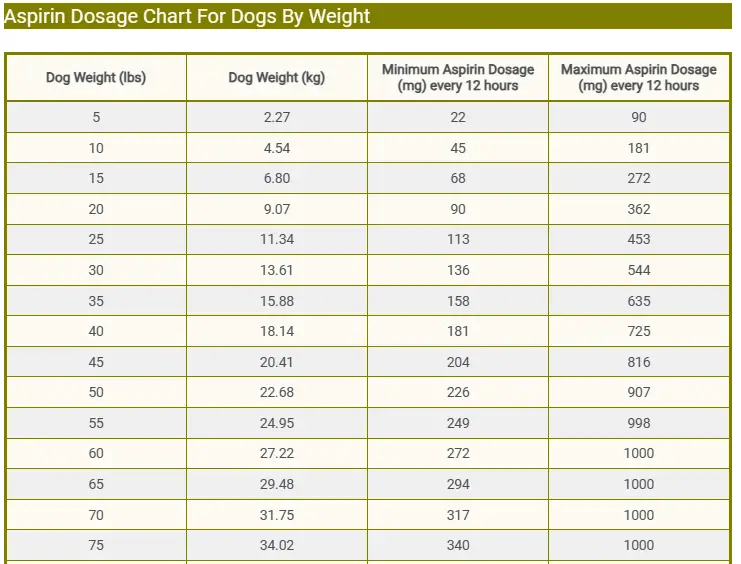
Aspirin Dosage Chart For Dogs By Weight
| Dog Weight (lbs) | Dog Weight (kg) | Low Aspirin Dosage (mg) every 12 hours | Maximum Aspirin Dosage (mg) every 12 hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2.27 | 22 | 90 |
| 10 | 4.54 | 45 | 181 |
| 15 | 6.80 | 68 | 272 |
| 20 | 9.07 | 90 | 362 |
| 25 | 11.34 | 113 | 453 |
| 30 | 13.61 | 136 | 544 |
| 35 | 15.88 | 158 | 635 |
| 40 | 18.14 | 181 | 725 |
| 45 | 20.41 | 204 | 816 |
| 50 | 22.68 | 226 | 907 |
| 55 | 24.95 | 249 | 998 |
| 60 | 27.22 | 272 | 1000 |
| 65 | 29.48 | 294 | 1000 |
| 70 | 31.75 | 317 | 1000 |
| 75 | 34.02 | 340 | 1000 |
| 80 | 36.29 | 362 | 1000 |
| 85 | 38.56 | 385 | 1000 |
| 90 | 40.82 | 408 | 1000 |
| 95 | 43.09 | 430 | 1724.0 |
| 100 | 45.36 | 453 | 1814.8 |
The above aspirin dosage chart for dogs by weight is provided for educational purposes only and should not substitute for veterinary advice. Always start with the minimum dose until your veterinarian prescribes an increase in dosage.
Related Post: Revolution Dosage For Dogs
Aspirin Uses in Dogs
-
Aspirin can alleviate mild to moderate pain in dogs, such as arthritis pain or discomfort following surgery or injury.
-
It may help lower the body temperature in dogs with fever due to infection or inflammation.
-
Aspirin’s anti-inflammatory properties make it useful in managing conditions like arthritis or certain skin disorders.
-
It can act as a blood thinner, beneficial in preventing blood clots in canines with heart disease or clotting disorders but must be used cautiously under veterinary supervision to avoid bleeding problems.
Related Post: Previcox Dosage For Dogs
Aspirin Side Effects in Dogs
-
Aspirin can irritate the stomach lining, leading to symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, or gastrointestinal ulcers.
-
Prolonged use or high doses of aspirin can cause kidney damage or worsen pre-existing kidney conditions in dogs.
-
In some cases, aspirin may lead to liver toxicity or exacerbate existing liver problems.
-
Aspirin’s blood-thinning properties can increase the risk of bleeding disorders, including gastrointestinal bleeding or bruising.
-
Dogs may experience allergic reactions to aspirin, resulting in symptoms such as itching, hives, or difficulty breathing.
-
Long-term use of aspirin in dogs has been associated with hearing loss, particularly at higher doses.
-
Although rare, Reye’s syndrome—a serious condition affecting the brain and liver—has been reported in canines following aspirin administration, especially in young puppies.
Which Dogs Should Not Take Aspirin.
Canines with the following health issues should not take Aspirin without veterinary recommendations.
-
Dogs with pre-existing health conditions such as kidney disease, liver disease, gastrointestinal ulcers, bleeding disorders, or clotting disorders.
-
Puppies, especially those under six months of age.
-
Pregnant or nursing dogs.
-
Dogs allergic to aspirin or those who have shown signs of allergic reactions.
-
Dogs taking other medications, especially corticosteroids, NSAIDs, or anticoagulants.
FAQs
Can I give my dog aspirin for pain relief without consulting a vet?
It’s not recommended to give your dog aspirin without consulting a veterinarian first. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your dog’s specific needs and health condition.
How often can I give aspirin to my dog?
Aspirin should be given to dogs no more than every 12 hours. It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and avoid overdosing.
What should I do if my dog experiences side effects after taking aspirin?
If your dog experiences any adverse reactions after taking aspirin, stop the medication immediately and contact your veterinarian. They can advise you on the appropriate course of action.
Are there any natural alternatives to aspirin for pain relief in dogs?
Yes, there are natural alternatives to aspirin, such as acupuncture, physical therapy, and dietary supplements. Consult with your veterinarian to explore these options for your dog.
How can I ensure safe medication usage for my dog?
To ensure safe medication usage for your dog, always consult with a veterinarian before administering any medication. They can provide guidance on dosage, potential risks, and alternative treatment options tailored to your dog’s needs.









![Can Dogs Eat Blood? 7 Side Effects [Expert Opinion]](https://petskor.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Webp.net-resizeimage-12.jpg)
